We have found that it is good for humans to take more than 24g of “dietary fiber” per day.
But actually eating 24g with food alone is very difficult. If you’re a cape, you have to eat about 1 ball + 1/4. That’s impossible. (-ω-)
Also, it is not a matter of saying “you can take as much as you want”. If you use the wrong method, your stool may become stiff and constipation may be promoted .
To begin with, there are two types of “dietary fiber”: “insoluble dietary fiber” that is insoluble in water and “water-soluble dietary fiber” that is soluble in water.
Both reach the large intestine without being digested, but the function from there is different.
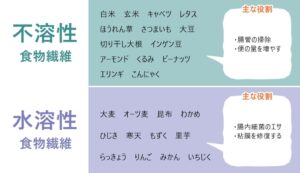
Insoluble dietary fiber swells several to several tens of times when it absorbs water, increasing the amount of stool and stimulating the intestines, and exercising as it is.
On the other hand, water-soluble dietary fiber becomes a moist gel when dissolved in water, making it difficult to raise blood sugar levels and lowering blood cholesterol levels . It is also worth noting that water-soluble dietary fiber also feeds good bacteria such as bifidobacteria.
When water-soluble dietary fiber is eaten by good bacteria and decomposed, it turns into acids called short-chain fatty acids.
The short-chain fatty acids include butyric acid, acetic acid, and probionic acid, all of which act as energy for the large intestine, prevent obesity and inflammation, and prevent diseases, eliminate bad bacteria, and repair injured year-end. It will also work for you.
The point is to take good water-soluble dietary fiber from the intestines, which helps the body to stay healthy.
(From “Intestinal Illustrated New Common Sense of Intestines”)
 Español
Español
 Inglés
Inglés
 Francés
Francés
 Árabe
Árabe



